The Graph
Updated on 2023-08-29T12:02:08.250509Z
What is The Graph?
The Graph was introduced in 2018 by Node Venture Inc and Edge. The Graph is a query layer of the decentralised web, that is, queries can be run on The Graph Network. Essentially, it is an indexing protocol for the decentralised web (web 3.0).
Subgraphs are developed and published by the developers. The subgraph is an open Application Programming Interface (or API) that can be used for querying by employing GraphQL.
Presently, The Graph is capable of supporting data from 22 networks namely, Ethereum, Avalanche, fantom, IPFS, Arbitrium, Celo to name a few. On the host, more than 18000 subgraphs have been published. Many developers have developed subgraphs for applications like Blancer, Gnosius, Liverpeer, Uniswap, Synthetix, Aragon, AAVE, DAOstack to name a few.

The data published on The Graph is also presented in a UI and other developers can make use of the subgraphs published on the network. In The Graph explorer, the subgraphs can be located, and the existing subgraphs can be utilised by the user.
The Graph network is managed by The Graph Foundation which comes under the management of the Technical Council. In The Graph ecosystem, StreamingFast and Edge & Node are a part among many other organisations.
Highlights
- The Graph was introduced in 2018 by Node Venture Inc and Edge.
- The data published on The Graph is also presented in a UI and other developers can make use of the subgraphs published on the network.
- In The Graph explorer, the subgraphs can be located and the existing subgraphs can be utilised by the user.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the working of The Graph?
Graph entered into a partnership with Polygon, and under the partnership, Polygon’s ecosystem would be chosen as the basis for the billing system. The Graph protocol (GRT) allows the users to query and index networks like IPFS, Avalanche, Celo and Ethereum.
The Graph has positioned itself as a leading blockchain query and indexing protocol and with constant growth, it has started dominating the indexing space. It has become a preferred platform for the development of decentralized applications (dApps) and IPF and products for Ethereum.
The Graph is positioned as a Web 3.0 product and The Graph protocol has unlocked the blue-chip status in the category of Web 3.0 products. Moreover, there are more than 20,000 developers that constructing subgraphs for application.
For deploying the new billing solution and providing scalability in it, proof-of-stake of the Polygon is used under the existing partnership.
Subgraph Studio provides a platform that empowers the developers to construct, test and publish the subgraphs and also manage the API keys.
Polygon proof-of-stake (MATIC) helps in the reduction of the gas cost for all the users of The Graph.
When a query is generated through API keys, then a fee is charged from the developers. All the fee invoices will be generated on the weekly basis on the Subgraph Studio.
With this technology and the features of the polygon, the process of querying data becomes seamless and the speed at which the new apps are developed increases significantly. Moreover, the cost of the whole development process does not increase.
The Graph takes advantage of the following features that are offered by Polygon:
- Enhanced Blockchain performance due to Polygon’s superior technology- Sidechain is one of the products that is offered by Polygon. Sidechains are essential in establishing connections with blockchain technology. They improve the overall performance of blockchains and allow transactions to be conducted in lesser time while incurring lower costs. Polygon can establish an interface with all types of blockchains.
- Providing an interconnected structure for a range of blockchains- With the framework of Polygon, the blockchain will be interconnected rather than working in isolation. This framework allows The Graph to reap the benefits of blockchains and Ethereum (tools and security).
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatibility- EVM is software that is provided by Ethereum through which developers can create their decentralised app. Due to ECM, Ethereum gained popularity and Polygon is compatible with EVM. SushiSwap and Aave are some of the apps developed on Polygon.
What does The Graph do?
Earlier, the developers had to build and operate on the indexing servers. For building an indexing server, hardware and engineering resources are required along with given significant consideration to the security issues. After the introduction of The Graph, a decentralised platform, all these issues were handled as The Graph can process, store, index and serves all data and maintains the integrity of the data. The process of data querying is made secure, reliable and fast.
What can be built on The Graph?
Advanced apps are being created on The Graph that enhances human coordination. Applications in Governance, DeFi, Grants and Philanthropy, marketplaces, social and Entertainment have been created.
When The Graph is combined with the Web 3.0 protocol, developers can gain access to the new features and can build dApps. The platform has the potential to solve the following issues:
Agency – The data, reputation and identity are safe.
Reliability – The platform guarantees that data can run forever on the public infrastructure.
Interoperability – It stands for switching between the applications and The Graph ensures seamless switch among the decentralised applications.
Money – The financial contracts and digital money can be traded on the network.
Security – The decentralised platform which maintains the anonymity of the users and stores the currency in the wallets ensures the privacy, security and safety of its users.
Governance – The users have voting rights in the whole process and the rules established on the network are transparent.
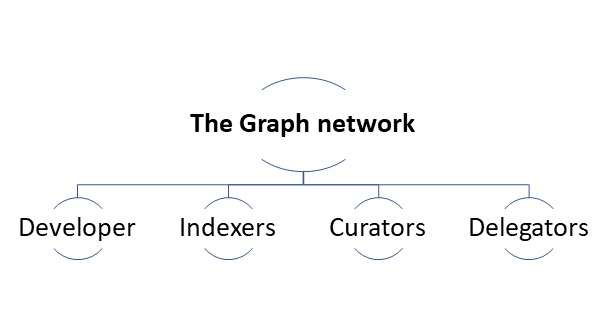
What is included in the network of The Graph?
Developer – These people are responsible for the creation of subgraphs, and they can also make use of the existing subgraphs in dApps.
Indexers – These people are responsible for indexing the data and serving the queries.
Curators – These people organise the data.
Delegators – The security of the whole network is ensured by the delegators.