Government Shutdown
Updated on 2023-08-29T12:01:32.387224Z
What is a government shutdown?
A government shutdown arises when the U.S. Congress fails to approve or settle disputes over the federal budget for the following fiscal year. It happens when non-essential U.S. government offices could no longer stay open owing to a lack of funds, services are not delivered, and government workers' wages are not paid.
Several federally run operations will be suspended during a government shutdown. A few organisations might remain open as long as they have cash reserves, but they would have to stop their operations when running out of money.
Moreover, if the president fails to sign the appropriations bills by the deadline, the government shutdown may occur. Usually, Congress adopts appropriations bills during the budget process, and the president of the United States signs them by September 30 for the new fiscal year, which commences on October 1.
Suppose the mechanism mentioned above fails to meet the deadline during the budget process. In that case, the president and Congress might enact a continuing funding resolution that maintains the appropriations at the present level. If all these processes are not finished on schedule, a shutdown may ensue, indicating a complete breakdown in the budgetary process.
Summary
- Government shutdown arises when the U.S. Congress fails to approve or settle disputes over the federal budget for the following fiscal year.
- The government shutdown has the potential to bring the economy to a halt.
- Non-essential government offices would be closed during a government shutdown, while a few essential personnel would carry on working, but their payment would be furloughed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Explain the term "government shutdown"?
Though a government shutdown may happen at the territorial, state, or local levels, the term "government shutdown" is usually associated with the federal government.
If a government shutdown happens, the U.S. federal government must limit agency services and activities, as well as suspend non-essential operations, including furloughing non-essential personnel.
Furthermore, a few agencies must continue to operate; if these services were to be halted, the public's safety, life, or health would be jeopardised. Personnel involved in essential operations may not be paid during this challenging period unless a special funding bill is passed.
Crucial federal agencies and services are unaffected by a government shutdown
The following is a list of key federal agencies and services that would continue to operate during a government shutdown.
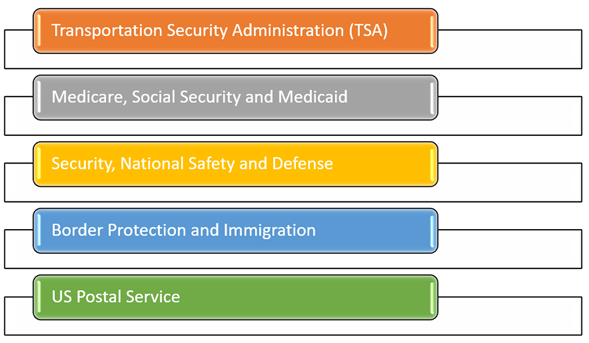
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Non-essential federal agencies & services impacted by a government shutdown
The following is a list of non-essential federal agencies and services severely harmed by a government shutdown and would be forced to shut down completely in an emergency.

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Since 1981, the United States has experienced 12 government shutdowns, ranging in length from one day to 21 days. Before 2018, the most recent U.S. government shutdown happened in 2013, lasting 16 days.
However, payments from government sources to civilians for veterans' benefits or unemployment insurance would not be interrupted throughout a government shutdown. The payment would be continued because these initiatives are funded by special allocated budgets from advanced Congressional appropriations. Furloughed federal workers could also submit a request for temporary unemployment benefits, but the procedure might take longer.
What are the repercussions of the government shutdown?
The repercussions of the government shutdown are widespread and can have a significant impact on residents' lives. For example, several federal processing activities could be severely hampered during the shutdown, and non-essential agencies that are unable to self-fund could be obliged to furlough or offer unpaid leave to their workers.
Furthermore, new loans for education, businesses, and houses might take longer or be extremely difficult to process during this challenging time. Unemployment benefits and new applications for social security benefits will be processed at a slower pace until the time situation improves. The military will not be exempt from the effects of the government shutdown. Death benefits would not be granted to surviving family members of service members who died in the line of duty.
On the other hand, food safety may be compromised, and children may become ill as a result. In addition, the government shutdown might lead the U.S. Department of Agriculture to postpone or stop inspecting food items and prevent the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) from banning dangerous goods.
The government shutdown has the potential to cause the economy to collapse. The entire cost and long-term impact of a government shutdown on the economy, however, could differ. For instance, in 2013, the U.S. economy lost US$24 billion because of a 16-day government shutdown.

Source: © Skypixel | Megapixl.com
What are real-world examples of a government shutdown?
2018
The latest and most prolonged government shutdown in American history occurred in 2018. As a result, Congress and President Donald Trump could not reach consent on funding for the fiscal year 2019. Consequently, nearly 800,000 government workers were affected by the shutdown.
2013
Around 850,000 workers, or 40% of the federal civilian workforce, were furloughed during the 2013 government shutdown. It had a significant economic impact, with GDP dropping by 0.3% due to lower government spending. Republicans utilised the government shutdown to delay the implementation of Obamacare. According to the Obama administration, the shutdown slowed economic growth by 0.2% to 0.6%.
1995 & 1996
In 1995 and 1996, there were two government shutdowns.
1995- Furloughs were imposed on 825,000 federal workers.
1996- Furloughs were imposed on 284,000 federal workers.
As per the Office of Management and Budget, both shutdowns cost US$1.4 billion, and it hugely damaged the economy.