Free Market
Updated on 2023-08-29T11:58:01.656649Z
A free market is an economic system where the laws of demand and supply are free from government intervention. In this system, the prices of goods and services are determined by the sellers and buyers after they have reached a consensus in an open market.

Image source: © Arturszczybylo | Megapixl.com
Summary
- In a free market, the government cannot interfere with the business activities carried out by individuals or private players.
- In a free-market economy, private individuals are not accountable to the government for the majority of their decisions.
- In such a system, rather than the central authorities, the private entities decide things such as - price and wages. Coercion free economic system is an essential characteristic of a free market.
- A free market represents a benchmark criterion, which does not exist. Economists have discovered a positive relationship between free markets and measures of financial security.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Who discovered the concept of a free market?
Adam Smith, a Scottish economist-philosopher, coined the term free market. According to Smith, a free market did not only mean a market free from government control but instead free from all forms of economic privileges and monopolies.

Image source: © Rfaizal707 | Megapixl.com
What are the Characteristics of a free economy?
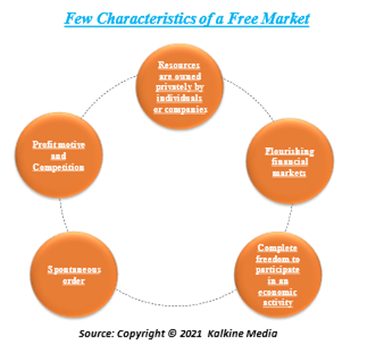
- Resources are owned privately by individuals or companies: In a free economy, a major portion of the resources is owned by private players or companies and not by the ruling government. The private entities take decisions related to the exchange of goods, labor supply and natural resources.
- Flourishing financial markets: In free markets, financial markets tend to meet the financial needs of those who cannot finance themselves. For example, there are individuals who believe in acquiring savings by not consuming all of their current wealth. On the other side, there are also some who deploy their savings to expand their business. They mainly gain profits by trading in stocks and exchanges. Furthermore, the presence of financial institutions is a prerequisite for the success of free market economies. Banks and brokerages provide investment facilities and serve as a platform for exchanging goods and services, thus benefitting the private players.
- Complete freedom to participate in economic activity: In a free market, the private players can choose to produce or consume any product.
- Spontaneous order: Free markets are also characterized by spontaneous orders. In free economies, complex transactional networks involved in production and distribution of goods and services are common. These networks are a result of decentralized economic decisions.
How can you say that a free economy is advantageous?
- Encourages Innovation: Depending on the customers’ preferences, companies can come up with new ideas to meet the change in the demands of the customers. In free markets, the businesses are not dictated by the government to produce a specific type of goods and services, but here the entrepreneurs conduct their own surveys to know what is precisely trending and is in the minds of the consumers. The resulting innovations lead to healthy competition in the market.
- Customers drive choices: In a free market, customers decide which product will be a success and which one will fail. Various factors like the consumers’ preference or choice for a product, its quality and affordability (price) are taken into consideration by the producers for a product to become successful in the market.
- Absence of red tape, bureaucratic hurdles, and government interference.
What are the shortcomings of the free market economic system?
- Businesses are driven by profit motives: Many times, businesses operate with a sole aim of making as much money as possible. They compromise with the customers or consumers' interest and do not adhere to ethical conduct. There are various examples where big corporate houses used cheap and bad quality products like cement for infrastructure projects, to earn high profit. This not only risks the lives of the common people but also wastes government spending. Therefore, it is argued that in an economic system, some amount of regulation is necessary.
- Market Failures: In the absence of regulatory legislation and zero interference from the government side, many times free market gets out of control. An example of this can be the Great Depression of 1930s which resulted in job losses, loss of income and homelessness.
- Some argue that Free Market gives rise to a black market, which is detrimental to the health of a country’s economy.
What do critics say about a free market system?
Critics of the free market often argue that such an economic system often leads to price fixing monopolies. It is also believed that free markets give rise to collusion between the competitors, and as a result, the consumers are at the receiving ends. Various economists also believe that due to these shortcomings, where certain market players exercise enormous powers, it has become even more important to enact antitrust legislation.
What is Antitrust law?
Antitrust law prohibits any business practices that are illegal, or unfair, or monopolistic in nature. In this aspect, the US, by way of variety of laws, has formulated policies to maintain fair competition among business enterprises. The most talked-about law is Sherman Antitrust Act, 1890. Under this Act, “every contract, combination or conspiracy in restraint of trade and commerce” is termed illegal.

Image Source: © Rfaizal707 | Megapixl.com
Similarly, antitrust legislation became more significant in Europe post the Second World War. In a capitalist country like the US, a mixed system consisting of both free market and command economy components prevail.
Which are the top five World’s strongest free market economies?
As per the Index of Economic Freedom, Singapore’s economic freedom score is 89.7, making its economy the freest in the 2021 Index. The other four countries in the top 5 positions are – New Zealand, Australia, Switzerland, and Ireland.