Dividend reinvestment
Updated on 2023-08-29T12:01:47.772655Z
What is dividend reinvestment?
Dividend reinvestment is a program in which the investors can reinvest cash dividends received in the underlying shares of the company on the date when the dividend is paid.
Through an investment company or a brokerage, the dividend reinvestment plan can be automated. The automation program is generally extended by the companies that are trading publicly to their shareholders.
Summary
- Dividend reinvestment is a program in which the investors can reinvest cash dividends received in the underlying shares of the company on the date at which the dividend is paid.
- Through an investment company or a brokerage, the dividend reinvestment plan can be automated.
- The automation program is generally extended by the companies that are trading publicly to their shareholders.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the working of dividend reinvestment?
Generally, an investor receives dividends directly into their bank accounts or through a cheque. In direct reinvestment, the shareholders have the option to not receive deposits in the bank account but rather invest the amount in the additional shares. The additional shares are brought from the company directly. The shares purchased come from the company’s reserve, therefore, they cannot be traded on an exchange. These shares can be redeemed from the company only.
To reinvest the dividend amount in the company’s share, the company, generally, does not charge any commission fee, or the fee is very nominal or discounted. The plan is focused on the existing shareholders, but some companies might offer the same to new investors as well. In such cases, the purchase amount is specified.
In dividend reinvestment, the dividend is not received, but still, it is seen as a taxable income.
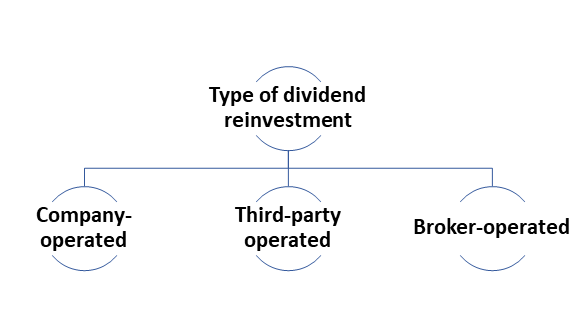
What are the types of dividend reinvestment plans?
Company-operated – The dividend reinvestment plan is handled by a specific department of the company.
Third-party operated – A third party is outsourced by the company for managing the dividend reinvestment plan. It saves the company’s time and cost.
Broker-operated – The plan is not offered by some companies, but brokers may extend the plan on some investments. Brokers purchase the shares from the open market and the charges are dependent upon the relationship with the client.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
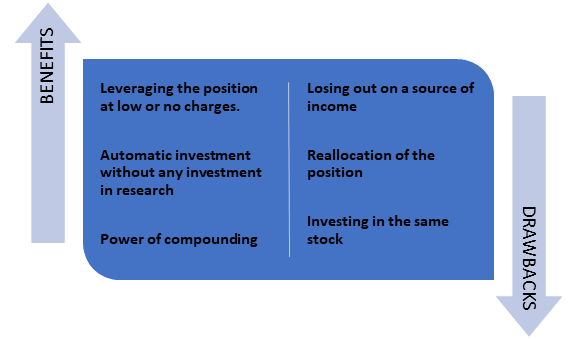
What benefits are associated with dividend reinvestment?
Leveraging the position at low or no charges – Generally, brokers do not charge any fee for reinvesting the dividend amount, that is, the investor will be able to purchase more shares at zero charges. Also, the investor can establish direct contact with the dividend-paying company about the dividend reinvestment program.
Automatic investment without any investment in research – If the investor has signed up for the automated dividend reinvestment plan, then the dividend amount will be invested in the company’s shares. Sometimes, the reinvestment amount is lower than the market price of the shares. The benefits are further accelerated if s good quality stock is held by the investor a longer duration. The exposure increases and little effort is required.
Power of compounding – Compounding is a powerful tool. This aspect further motivates investors to sign up for dividend reinvestment. For instance, each reinvestment will increase the overall reinvestment amount and thus the dividend income.
What drawbacks are associated with dividend reinvestment?
Losing out on a source of income – In case the main source of the income is the dividend income, then it is not a good idea to sign up for the dividend reinvestment plan. So, when looked at one’s portfolio, the dividend income will be a priority over reinvesting the same.
Reallocation of the position – When the dividend income is reinvested, then the position of the shares increases within the portfolio. It might create an imbalance within the portfolio. If the investor observes that the stock position has reached the desired level, then the reinvestment plan should be turned off and the income should be enjoyed or reinvested in other shares.
Investing in the same stock despite personal preferences – If the investor does not wish to make an investment in the stocks at a particular duration due to reasons such as the stock being overvalued, then the dividend reinvestment should not be taken up.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What is the tax treatment in dividend reinvestment?
When an investor receives a dividend, then it is considered as taxable income. Even if the investor is part of the dividend reinvestment plan, then also the dividend received is seen as the taxable income. However, if the dividend is paid in the form of stocks, then it is not included in the tax calculation. Tax is charged on the stock dividend, only when those shares are sold in the financial market.
When should the dividend reinvestment not be signed?
In these situations, the dividend reinvestment does not make any sense:
At the time of retirement – After the retirement, the other sources of income should be considered like pension, social security and so on. If these incomes are not enough to meet the requirements, then the dividend should not be reinvested.
Dividend-paying security is not performing well – In the financial market, it is common to observe huge swings in stock prices. If the dividend-paying security is no more adding value to the portfolio, then dividend income becomes a priority over the reinvestment in the same security.
Diversification is the aim – If the investor aims at diversifying the portfolio, then the dividend income should be reinvested in other securities rather than taking a position in the single security.
Portfolio management – With the power of compounding, in no time, the position in a particular security might get overweighted. The overweight of any security can expose to a higher amount of risk, that is, if the security performs well then, it’s a benefit, but if it performs poorly, then the loss amount will also increase. Therefore, it is essential to manage a portfolio in an efficient manner.