The World Bank
Updated on 2023-08-29T12:02:07.693961Z
What is the World Bank?
The World Bank is a global financial organisation that assists developing countries to grow and prosper by raising funds, guidance, and analysis. The bank is primarily a development bank that aids low- and middle-income nations in their fight against poverty.
Highlights
- The World Bank is committed to assist developing countries in their economic development by providing funding, guidance, and analysis.
- The World Bank works to eradicate poverty by fostering sustainable prosperity and assisting in the reconstruction of war-torn countries.
- In developing countries, it wants to strengthen education, health, and infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do we require the World Bank?

Source: © Igenkin | Megapixl.com
The World Bank, based in Washington, D.C., is the world's largest provider of financial aid to developing countries and is aligned with the United Nations (UN). It offers technical support and policy guidance and oversees the implementation of free-market reforms on behalf of foreign creditors.
It plays a key role in shaping the global macroeconomic agenda and reforms in developing countries, alongside the World Trade Organisation (WTO) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
The World Bank is made up of two distinct bodies and is not a conventional bank. One of them is the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), which offers credits, loans, and grants to qualified governments to assist individual economies in their growth. In addition, low-income countries may get low interest or zero-interest loans from the International Development Association (IDA).
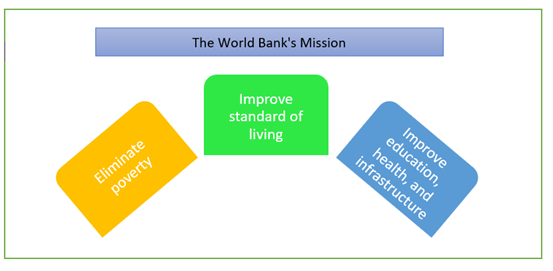
What is the World Bank's mission?
Its first aim is to eradicate extreme poverty. By 2030, it expects that fewer than 3% of people will be living on less than $1.90 a day.
Its second mission is to foster stability for everyone. It aims to raise the living standards of the bottom 40% of the population in each nation. The World Bank has sponsored over 12,000 projects since 1947.
It aims to improve education, health, and infrastructure and provide resources to modernise a nation's financial industry, farming, and management of natural resources.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
It has a long-term goal of reducing poverty sustainably, and it works toward that goal by converting rich country capital into poor country development.
The World Bank works on many areas to accomplish these goals:

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What is the World Bank's history?
In 1944, the World Bank was formed at the Bretton Woods Conference, also recognised as the United Nations Monetary and Financial Conference, to establish a global financial system after WWII. It started operations in June 1946.
A joint international monetary system, the establishment of the World Bank, and the development of the IMF were all part of the Bretton Woods Agreement.
Its first loans were intended to help rebuild Western Europe following WWII. It was a major player in funding investments in infrastructural projects in developing countries, such as bridges, water and sanitation facilities, hydroelectric dams, maritime ports, and airports, beginning in the mid-1950s.
In the 1970s, President Richard Nixon put an end to the Bretton Woods System. But, on the contrary, the IMF and the World Bank continued to operate and prospered by offering global assistance.
The World Bank and its affiliate organisations work under their own rules and produce their own proprietary financial assistance products to aim for countries' foreign capital needs. About 10,000 employees work for the World Bank, which has around 120 offices worldwide.
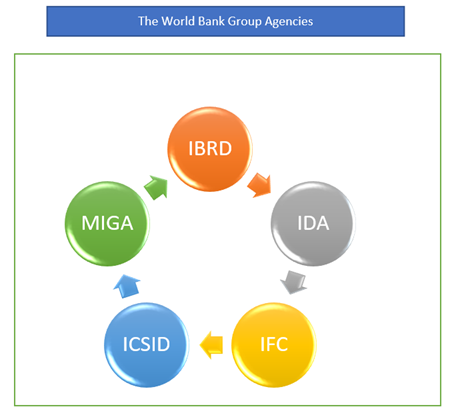
What are the five World Bank Group agencies?
- The International Development Association (IDA)
IDA provides governments of the world's poorest countries with interest-free loans, which are known as credits.
- The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD)
IBRD provides loans to governments in middle and low-income countries.
- The Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA)
MIGA facilitates foreign direct investment (FDI) to strengthen the economy, alleviate poverty, and raise living standards in developing countries.
- The International Finance Corporation (IFC)
IFC assists developing countries in achieving long-term growth by funding investment, mobilising resources on international financial markets, and offering business and government advisory services.
- The International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID)
For investment disputes, ICSID offers global conciliation and arbitration services.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What are the advantages of the World Bank?
- It gives monetary and technical assistance to developing countries to reach the desired goals.
- It provides low-interest loans to underdeveloped countries to help them combat poverty at rates lower than those charged by normal banks. It may also be able to include grants and interest-free credits.
- The bank's key goal is to close the gap between the rich and the poor and to ensure that funds are allocated in such a way that poor countries can sustain their economies.
- Many vulnerable people in the country have benefited from the bank's assistance by providing them with necessities such as healthcare and food to combat hunger and education.
- As a result of the World Bank's efforts, trade barriers are being reduced, resulting in more trade between nations and increased wages.
- One of the World Bank goals is to empower women in terms of economic development and labour force participation, and the bank advocates for reform.
- The World Bank has addressed the problem of unemployment by launching projects in different countries that promote and finance programmes that motivate adults to pursue entrepreneurship as a means of eradicating poverty.
- To ensure food security, the World Bank initiated an agricultural development programme, focusing on developing countries.
- The World Bank, through global alliances, provides relief to certain debt-burdened countries.
- In most cases, low-income families, particularly women and children, are denied adequate health care in developing countries. The World Bank puts a focus on good nutrition and maternal health.
What are the World Bank's drawbacks?
- Rich or economically dominant countries wield greater influence over poor countries, resulting in inequity in the assistance provided.
- The bank has been chastised for its ineffective policies and poor response times.
- The World Bank loans have unfavourable terms attached to the assistance given.
- Only the major shareholders participate in decision-making at the World Bank, resulting in a dictatorship.
- The World Bank's free market would have a negative effect if it was not properly enforced.