Monetary Assets
Updated on 2023-08-29T12:01:17.676379Z
What do you mean by Monetary Assets?
Monetary Assets have a constant value in currency units and can be easily liquidated into cash/cash equivalents. As a result, the dollar value of monetary assets remains firm even during inflation when the currency's purchasing power decreases. The value of monetary assets is not affected either by depreciation or appreciation.
The assets can be easily converted into a fixed or precisely calculated amount of money, including cash on hand, accounts receivable (AR), bank deposits and notes receivable.
Monetary assets are also regarded as current assets and are thus mentioned on a company's balance sheet. The recorded value of the monetary assets can never be restated on the financial statements.
Summary
- Monetary Assets have a constant value in currency units and can be easily liquidated into cash/cash equivalents.
- The recorded value of the monetary assets can never be restated on the financial statements.
- Non-monetary assets do not have a fixed dollar value and cannot be easily converted into cash.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the characteristics of Monetary Assets?
- Fixed in value but may also end up with a decline in absolute value
The value of monetary assets is constant in terms of dollars; however, they may change in real terms (relative change in purchasing power). For instance, if a business has $40,000 as cash, the value after a year will also remain the same, i.e., $40,000. However, in future, there is a possibility that due to inflation, the thing which cost $40,000 last year will cost more than $40,000 in the current year. This suggests that there has been a drop in real terms even though the dollar amount remains constant.

Image Source: © Mazzel1986 | Megapixl.com
- Restated value in financial statements
The recorded value of monetary assets cannot be restated in the financial statements. At the same time, non-monetary assets are subject to appreciation or depreciation depending on the market conditions.
Other characteristics of monetary assets include – higher liquidity, which can be easily converted and can be used as working capital. Furthermore, they are not subject to appreciation or depreciation.
What can be the examples of Monetary Assets?
Few examples of monetary assets are:
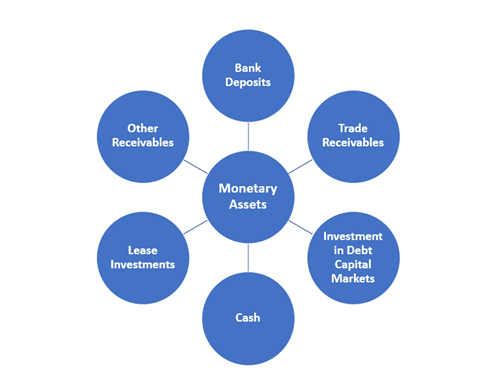
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
- Cash: Cash can be used in the sale and purchase of goods and services or can be used as debts. Cash can be in the form of a dollar. Though the macroeconomic factors in an economy like inflation can affect the purchasing power of cash, it has a fixed value.
- Bank Deposits: Bank deposit is the money placed by an individual with the banks or any other financial institution. The money is deposited in accounts, like - checking accounts, money market account and savings account. This money which is deposited in the bank accounts is regarded as a monetary asset. This money can be withdrawn from the accounts by an individual in cash, as and when required.
- Trade Receivables: Trade receivables refers to the monetary amount owed to a business by its customers for the goods and services that have been provided but for which the payment has not been made yet. This amount which is to be paid by the customer to the business in return for the goods and services, will not change but will remain the same even when their value alters during the receipt of the payment. A company's balance sheet depicts account receivable as an asset.
- Other Receivables: Other Receivables generally refer to the residual trade or non-trade receivables that a firm has not specified and thus do not fulfil the criteria of being classified separately. Since other receivables are settled through cash mode, their value does not undergo any change with time.
- Investments in Debt Securities: Investment in debt capital will remain the same over time. These investments remain unchanged even at the time of their maturity.
What is the usage of Monetary Assets for business purposes?
- To meet daily expenses – A business needs money in real terms to perform normal business operations. This money is used to meet day to day expenses and for paying salaries to the workers.
- Monetary assets can also be used as working capital: Monetary assets can also be used as working capital to make repayment to the creditors, give short-term loans, and make advance payments to employees and others.
- To maintain Liquidity – Regular cash flow is a prerequisite for a business. Moreover, there are certain risks and uncertainties associated with businesses. It is, therefore, necessary to have sufficient cash to meet any unplanned expenditures.
- To reduce risk or uncertainty.
- Monetary assets assure investors and stakeholders that a business owns a certain amount of liquid funds. So, when there is a financial crunch, liquid funds act as a safety tool for stakeholders.
- If a company possess sufficient monetary assets, it assures the creditors that their money will not go anywhere and will be repaid in a time-bound manner.
Is there any asset that can be either monetary or Non-monetary?
Some assets can either be monetary or non-monetary. An example of this can be prepayments or advance payments. A contract with a third party decides whether Prepayments or advance payments are monetary or non-monetary assets. The third party generally is the one to which payment was made. Suppose the contract says that the prepaid amount is not repayable/returnable, or there is no contract, and the chances of getting back the amount are meagre. In that case, it is considered a non-monetary asset. On the other hand, investments in preferred shares are considered as monetary assets if there exists a clause in the contract, according to which, just like a debt, the issuing entity must undertake the redemption of preference shares after a specific time, in future. Or else, investments in preferred shares will be considered as non-monetary assets.
What are the Non-monetary assets?
