Maintenance Margin
Updated on 2023-08-29T11:56:52.512934Z
What is meant by the term maintenance margin?
Maintenance margin refers to the extent to which capital should be maintained in the margin account to hold a trading position or to avoid a margin call. This margin is also referred to as a variation margin or minimum maintenance margin or maintenance requirement. It is the minimum amount of margin balance required in the margin account to maintain the futures position valid.
The minimum amount of money that the broker or exchange requires the investor to have in the account for losses to be covered is known as the maintenance margin. Anything less than that puts the broker in danger of not having enough money to be deductible in the event of a loss.
Highlights
- Maintenance margin refers to how the borrower should maintain capital in the margin account to hold a trading position or avoid a margin call.
- Maintenance margin is a cover that a lender seeks to be sure that the borrower will pay back even if the market is on a downswing, the lender would still be covered from losses caused due to price fluctuations in the securities in the margin account.
- The maintenance margin is a percentage lesser than the initial margin requirement.

© Darren4155 | Megapixl.com
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a margin account?
A margin account is a leveraged trading account, i.e. a trader need not pay from his pocket the total value of the investment to trade. Simply put, a margin account helps an investor borrow money for investment against the investments held in the margin account. The investor can make a stipulated deposit and borrow the rest. The stipulated deposit is called the margin- it is a percentage of the total value of the financial instrument that the borrower aims to invest in.
How does maintenance margin come into play with respect to margin account?
Let us try to understand things with the help of an example. Suppose an investor wants to buy 1000 shares of Company M at the price of US$ 10 per share. However, the investor does not have the entire amount of US$ 10000. So the investor sets up a margin account with a brokerage firm. The brokerage firm will agree to let the investor acquire the shares by only putting in a portion of this total purchase price of US$ 10000.
Suppose the customer's initial margin requirement is 40% of the total purchase price. In this case, the investor would need at least US$ 4,000 in the margin account, and the investor can borrow the balance amount of US$ 6,000. The investor would typically be charged a nominal financing fee against the borrowing facility provided.
The maintenance margin is typically few percentage points lesser than the initial margin requirement. The investor must have the maintenance margin in their margin account to save themselves from a margin call. Let us suppose that the expected maintenance margin requirement by the brokerage firm is 25%. Therefore, the investor’s maintenance margin will be US$ 2,500.

© Karpenkoilia | Megapixl.com
Then later, if there is a recession in the economy and the share prices of Company M decline by 20%. Now each share is valued at US$ 8. Thus, the 40% initial margin requirement would now stand at US$ 3,200. However, the 25% maintenance margin is US$ 2,500. While the margin account would have dropped to US$ 2,000 due to 20% drop in the share value. This means that margin call will be triggered because the margin account only has US$ 2,000.
A margin call is triggered due to the inability of the borrower to maintain the margin requirement of 25%. In such a scenario, the borrower can either deposit the balance cash to the margin account or add permissible securities (whose value is worth the balance) to the margin account or liquidate the stocks such that the maintenance margin is hit.
Why is maintenance margin significant for the lender or broker?
Maintenance margin is a cover that a lender seeks to be sure that the borrower or the investor will pay back the money even if the market is on a downswing, the lender would still be covered from losses caused due to price fluctuations in the securities in the margin account.
What are the types of margin requirements?
In the case of margin trading, margin requirements may be in the form of initial margin or maintenance margin. At the outset, an initial margin is mandatory for the broker to sign up for the trade. On the other hand, to be able to continue the deal between the broker and the investor, a maintenance margin is mandatory.
The initial margin is always higher than the maintenance margin. The investor needs the maintenance margin to avoid the margin call from the broker or lender.
What is meant by the term margin call?

Image Source: © Avictorero | Megapixl.com
The margin call price can be estimated using the following formula-
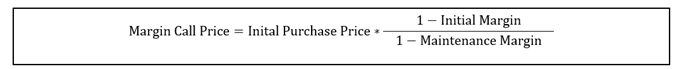
In this formula,
- The initial purchase price is the price at which the investor bought the security.
- Initial margin is the minimum percentage that the investor must pay
- Maintenance margin is the amount of equity that the lenders expects the borrower to maintain in the margin account.
When a margin call is triggered, the borrower has the option of adding more cash or adding more securities, clearing a portion of the principle from the outstanding balance, or placing a sell order.
We can understand with the help of an example when a lender can trigger a margin call. Y wants to buy securities worth US$ 500 with an initial margin of 60%, i.e. Y will use US$ 300 as the initial margin and the balance US$ 200 will be borrowed from a broker. If the maintenance margin is 30%, then the margin call price will be estimated using the above formula where
Initial purchase price= 500
Initial Margin= 60%
Maintenance Margin= 30%
So a margin call will be triggered if the price of the security declines below US$ 285.72.