Encumbrance
Updated on 2023-08-29T12:00:32.697323Z
What is meant by encumbrance?
Encumbrance refers to the restriction placed on the usage of certain funds. This definition of the term is used in accounting. These funds are restricted for a specific liability. However, when used for real estate, the term refers to a claim on a property that is not placed by the owner but by a secondary party.
The most common kinds of encumbrance applied in the real estate sector include mortgages, easements, and property tax liens. Encumbrance can be non-financial when it is applied to personal property.
Encumbrance affects the transferability of a property and limits its free usage until the burden is lifted.
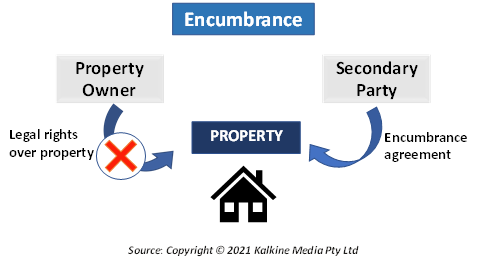
What are some examples of encumbrance?
Mortgages are obvious examples of encumbrance. If a homeowner does not keep up with the mortgage's repayment, the lender can foreclose the property. This means that the lender can take away the ownership rights of the property from the borrower.
Other examples include lien, or a claim on a property along with zoning laws and environmental restrictions.
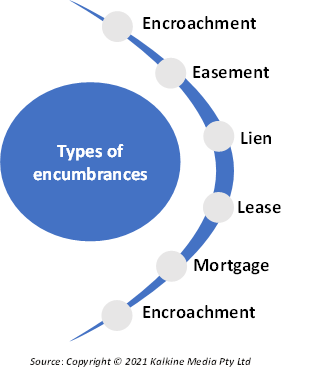
What types of encumbrances are there?
Encumbrance has various forms when it comes to real estate depending on its usage. Each form is intended to protect all parties and clarify the roles involved and what the parties are entitled to.
- Encroachment: This occurs when a party that is not the owner of a particular property tries to intrude by overstepping the boundary. An example of this can be a property owner building a porch that extends the permissible limit or building a plantation beyond the walls of one’s house.
Such type of encroachment is an encumbrance for both the one partaking in the encroachment as well as the victim of the encroachment. The victim’s free use of his own property is encumbered whereas the encroaching party does not hold the title to the land on which this extension has been built on.
- Easement: Easement is one party’s rights to modify the property of another party. On the contrary, easement can also be used by a party to prevent the owner of the property from making any modifications to the property in question.
An easement can be more beneficial to the secondary party rather than the owner. The easement allowing modification powers to the secondary party is known as affirmative easement while the preventive easement is called negative easement.
- Lien: A lien is a type of security that is beneficial in case of an unmet obligation. Lien allows ownership rights to the creditor in case of default on the part of the borrower.
This right allows the lender full access to the collateral, which he can then sell to gain back some of the money he had lent. Similarly, tax liens are also imposed by the government to encourage tax payments while judgement liens are secured against the assets of the defendant.
- Lease: One of the simplest kinds of encumbrance is lease, which includes an agreement to rent out a property for a specified period. In this special type of rental agreement, the owner does not lose the title to the property. However, the lease greatly decreases the owner's powers, thus refraining him from performing several actions.
- Mortgage: A mortgage allows the bank to take control over the collateral in case of default. It can be understood as a claim held by the lender on the collateral till the time the entire amount has been repaid.
In case repayment is not made, the lender can foreclose by evicting the inhabitants and taking full control of the house.
- Restrictive Covenant: Restrictive covenant refers to an agreement written into the buyer’s deed of property. This agreement alters how much control the buyer has on this property and how he may use it.
Even after the building is sold, the previous seller can introduce certain restrictions like holding onto the house's structural integrity and shape, etc.
What is an encumbrance certificate?
An encumbrance certificate is a certificate of assurance stating that the underlying property is free from any legal or monetary liability. This includes liabilities like a mortgage or an uncleared loan.
Such a certificate is essential for the buyer of a house to ensure that his legal rights are secured over the title of the house. An EC also ensures that the new homebuyer can obtain loans from most banks and financial institutions.
What needs to be kept in mind before buying an encumbered property?
An encumbered property can be a tricky one to purchase without full knowledge of the subject. Homebuyers may sometimes refrain from purchasing an encumbered property altogether out of fear of losing out on legal rights.
However, it is important to note that not all types of encumbered property could put the buyer at a loss. Thus, it is a great practice to be fully aware of the contents of an encumbrance agreement.
On the contrary, certain encumbrance agreements may hold additional responsibilities that can be passed onto the new buyer. Thus, if they are not settled before closing, it can be a wrongly imposed burden on the new house owner. These may include financial encumbrances apart from the mortgages. It is always good to consult either a real estate professional or a legal advisor in such instances.
How is encumbrance used in accounting?
In accounting, encumbrance sets aside certain funds to pay for forthcoming liabilities. With an encumbrance, firms and institutions may sometimes have an illusion of higher number of funds available with the company.
These funds generally can not be used for any purpose other than for what they are intended for. This type of budgeting ensures that businesses and institutions do not overshoot their limit by using them for expenditures or other transactions.