Stock Dividend
Updated on 2023-08-29T11:56:23.501092Z
How can stock dividend be defined?
Stock dividend can be defined as the dividend paid to the shareholders of a company that is made in the form of shares instead of cash. The greatest advantage of a stock dividend is that a company does not lose its liquid cash while paying to its shareholders.
The stock distribution method is carried out by providing a fraction of the existing shares to the shareholders. For instance, if a company offers 3 percent of shares, it implies that for every 100 shares owned by the shareholder, he or she is rewarded with extra three shares as a reward for his or her investment.
Summary
- Stock dividend can be defined as the dividend paid to the shareholders of a company that is made in the form of shares instead of cash.
- The stock dividend is preferred by those companies who either do not have enough liquid cash or would utilise the cash for other operational activities.
- The benefits of stock dividends are maintaining the liquid cash fund, taxation benefits and maintaining a fair price for investing.
- The disadvantages of stock dividends are market assumptions and spreading misinformation, and involvement in risky projects.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ)
How does stock dividend work?
Unlike a cash dividend, a stock dividend is a method of paying back to the shareholder of the company in the form of additional shares instead of cash. The board of directors and management of the company is responsible for making the decision whether they would like to give cash dividends or stock dividends to its shareholders.
A company generally offers cash dividends to their shareholders when they do not have enough liquid cash to spare for cash dividends. Stock dividend allows a company to keep aside their liquid cash and pay its shareholders in the form of stocks instead.
Stock dividends are also beneficial to the investors with respect to the tax payments. A shareholder is never taxed for a stock dividend, and it is only taxed in case of a cash dividend.
Moreover, the stock dividend that is received by the shareholder is not allowed to sell for a certain period of time. This period is known as the holding period, which starts on the day after the dividend is received. This holding period helps the shareholder to understand the tax treatment for dividends received.

Image source: © Moth | Megapixl.com
What is the dilution effect in stock dividend?
In stock dividend, the dilution effect refers to the decrease in the total value of shares of the company while approving stock dividend to the investors. For example, let us assume that company A offers a 3 percent stock dividend to its existing shareholders for every 30 shares that they own. For doing so, company A increased the total number of available shares in the company while the value of each share gets diluted so that the net value of the shares remains constant.
If an investor owns 100 shares, he is approved of 103 shares as his stock dividend. However, the market value of the shares remains constant due to the dilution effect. This feature of a stock dividend is also quite similar to a stock split.
What are the benefits of a stock dividend?
- Maintain the liquid cash fund
The companies that lack enough liquid cash often opt for stock dividends. This way, they can collect funds as well as repay the investors with the available stocks of the company. Generally, a stock dividend is chosen by those company which do not have a steady flow of cash or are in their initial stage. They mostly utilise their revenue for the upcoming operational activities of the company.
Stock dividends are usually beneficial to the shareholders from the aspect of tax payment. The taxes are not chargeable in the case of stock dividends. Unlike cash dividends, which is considered as a yearly income and is taxed, the stock dividend is free from all taxes, which makes it appear superior to cash dividends to most investors.
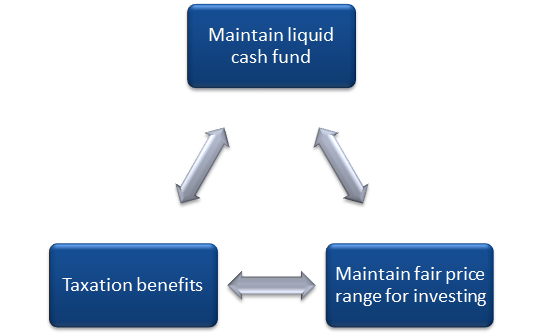
Image source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
- Maintain a fair price range for investing
As we have already explained, the dilution effect is where the company increases the number of shares and balance it out by lowering the values of the shares. Thus, when the prices of the shares decrease, it becomes easier for new investors to come forward and buy shares. Therefore, it can also be said that stock dividends attract new investors.
What are the drawbacks of a stock dividend?
- Market assumption and spreading misinformation
The market might assume that a stock dividend indicates a lack of cash and financial crisis. The investors might find it risky to invest in that company and would rather refrain from investing at all.
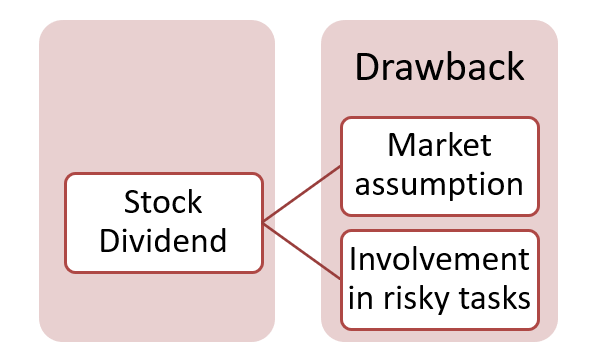
Image source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
- Involvement in risky projects
Approving a stock dividend instead of a cash dividend may indicate that the company is involved in some risky transactions. Therefore, it can cause doubt about the company.
What is the difference between a stock dividend and a cash dividend?
- Stock dividend: Stock dividend refers to the payment of the company' share through stocks of shares to the shareholders. The management or the board of the company decides to do so when there is a lack of liquid cash in the company funds.
- Cash dividend: Cash dividend refers to the payment of the company's share through cash to the shareholders. Companies can also do so when they have enough liquid cash in their funds. Usually, the matured companies prefer cash dividends as they have a steady flow of cash.