Dividend
Updated on 2023-08-29T11:58:44.770668Z
What are dividends?
Investors makes an investment with a hope of receiving returns. Dividends are part of the profit given out to shareholders as a reward for investing in equity. The board of directors declare dividends and it requires the consent of the shareholders. Dividends are paid only after paying all other creditors and complete debt financing. Even after these payments, the company can exercise its discretion on whether or not to declare dividends, instead retain the earnings. The company can have the choice to plough back the profits for the purpose of growth and expansion of the business.
Summary
- Dividends are part of the profit given out to shareholders as a reward for investing in equity. The company can exercise its discretion on whether to declare dividends or to retain the earnings.
- The dates between declaration date of dividend to actual payment date may see fluctuation in share prices.
- Dividends may be given out in the form of cash, pro rata stocks, property or special dividends.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is dividend given out?
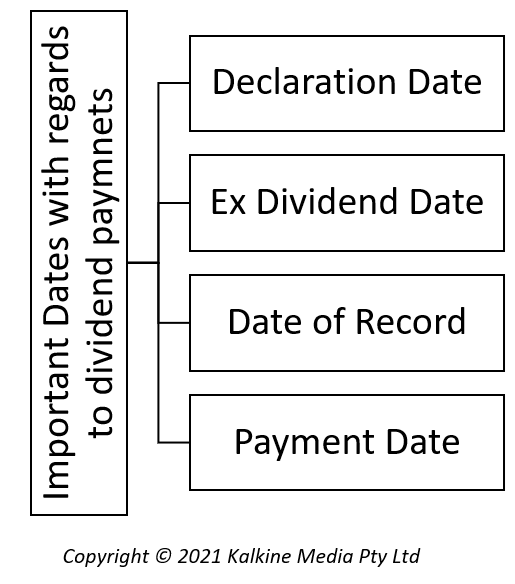
Let us suppose that ABC Company announced dividends along with results on 10th April. This is Typically the announcement date and is the date when a company’s results are announced and the management proposes declaration of dividend. This, as stated above, must first be duly approved by the board of directors after consideration of other factors and then is passed for approval by the shareholders.
Since shares can be easily traded over the stock market and shareholders may change, an Ex-dividend date is a must. The holder of the stock as of the ex-dividend date will alone be eligible for the dividend and after this date the eligibility expires. Here let us assume that ABC company has announced 10th May as the ex-dividend date. Hence shareholders owning shares of ABC company on the last working day on or before 10th May would only be considered for the payment of dividends.
Suppose the share is traded on the 10th of May and X buys it from Y then the share price paid by X are adjusted for the dividends which Y receives.
Typically, in stock markets, any transaction takes a settlement period of T+2 days. So if the above case of trade between P and Q happens on say 9th of May, it will get settled on 11th of May. And hence, this is the date when the shareholder’s register gets updated with Q’s details instead of P. This is where the record date is of essence. Record date is the cut-off date when the company takes the list of shareholders to whom the dividends have to be paid out. Usually, the record date is one day after the ex-dividend date so that the transactions on the day prior to the ex-dividend date get reflected in the company books.
Finally, the dividend actually gets credited to the investors’ accounts on the payment date. Usually, the payment date is a week or more after the record date.
When a company earns profits, it first budgets for needs like acquisition, expansion, mergers etc. and allocates the required amounts. Then, with the consent of the board of directors, excess profit is declared to be given out as dividends. The company then declares the amount of dividend and the date on which it would be paid out.
What are the types of dividends?
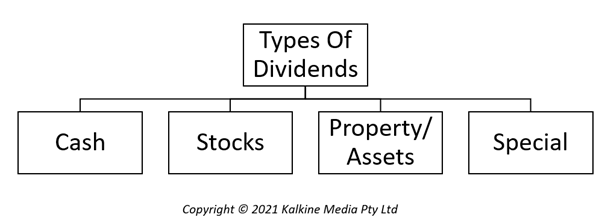
Once a company has decided to pay dividends, it can choose to do it in four ways. The most common option is a cash dividend where the company pays the dividend per share. Certain companies chose to split this based on their structure of reporting. For instance, a company might declare an interim dividend for each of its interim reporting period and then announce a final dividend at the time of full year results.
The second common option of paying dividends is a stock dividend or more commonly known as bonus shares. Rather than paying the dividend in cash, the company could reinvest the amount in the company and issue new shares of similar value to the existing shareholders.
In rare occasions, primarily when a company is liquidating, it might choose to pay dividends to its shareholders in property or assets.
Special dividends are dividends announced by a company when it makes out of turn dividend announcements in addition to the recurring cyclical ones. The sizes of such give outs are usually more significant than those in the regular due announcements.
Do dividends impact the value of a company’s shares?
Dividends have high impact of value of shares. If company lowers its dividends for any reason, it may not be perceived well by the public and they may be motivated to invest elsewhere. Thus companies try to keep it stable even if it may make high profits or low profits.
Dividend Per share, Dividend yield and dividend pay-out ratio are prominent values used by investors to judge the dividends they may receive from a stock.
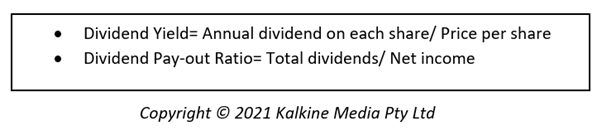
When an investor invests in a company, he or she may judge on the basis of dividend yield. Dividend yield is annual dividend per share divided by share price. Since dividend is a return that the investor would receive thus he or she discounts the cash flow accordingly before making the decision to invest.
Dividends also are indicative of a company’s stability of cash flows.
Investors who park their money in blue chip stocks rely on dividends as a regular and stable source of income
Companies that allow the benefit of consistent dividends enjoy a certain amount of trust in customer perceptions and hence there is more demand for their shares thus driving up the prices.
For a company that has declared dividends, people will be agreeing to pay premium to buy the stock before e dividend date thus driving up the share prices for this reason.
Declaration of stock dividends too can drive up the prices of the shares as investors would want to earn stock dividends. However, such speculative rise or fall in price is usually temporary and adjusts itself around the ex-dividend date.