Days Sales in Inventory
Updated on 2023-08-29T11:54:16.859911Z
What is Days Sales in Inventory?
Days sales in inventory (DSI) is a metric in finance that shows the average number of days a firm utilizes to turn its inventory (including all works in progress) into sales. It is also called Days in inventory (DII). It is a liquidity indicator for the inventory a firm is holding. Another way of looking at it is to consider it as the number of days the current inventory stock will last. A high DSI possibly means a firm is inefficient in managing inventory or the fact that it is facing difficulty in sales.
Summary
- Days Sales in Inventory shows on average how many days a firm takes to sell off inventory.
- Poor management of inventory is indicated from a High DSI number, and a low DSI number shows inventory and sales optimization.
- DSI is a very good measure of liquidity and efficiency of the inventory a firm holds along with its work in progress.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)-
How is Days Sales in Inventory computed?
The Formula for computing the ratio is as follows.
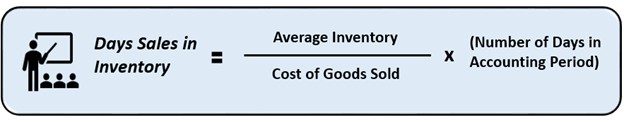
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Daily Sales in Inventory is determined by dividing the average inventory (including work in progress) balanced by the cost of goods sold. The resultant is then multiplied by the number of days in the reporting or accounting period. It shows the average number of days a firm requires to convert its resources into cash.
Another way of computing it is:
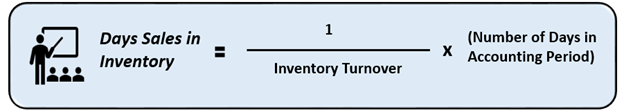
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
It can be taken as the inverse of inventory turnover for a given reporting or accounting period. This Formula has the underlying logic of lower the inventory turnover, higher the amount of inventory with the firm and vice versa.
Two different versions are depending upon prevalent accounting practices in the firm or industry. While version may be used to get the average value of Start Date Inventory and End Date Inventory, the other may be used to get DSI value during a given period.
Example-
Suppose there is a popular retail company in your neighbourhood, the Hulk Furniture Mart, since 2010. As of the closing of the year 2020, its’ financial reports mention opening and closing inventory numbers for the year. The average inventory comes out to be US$80,000, and the cost of goods sold computed internally is US$400,000.
If you want to know the Days Sales in Inventory (DSI) for Hulk Furniture Mart, you can simply take the numbers and substitute them in the previously shown Formula.
Considering 360 days in the year for computation, you will see that Hulk Furniture Mart has 72 days of sales parked in inventory. It means Hulk Furniture Mart takes on an average 72 days to sell its stock of furniture and convert it into useable cash.
Alternatively, if these numbers were not available and only the Inventory turnover ratio of Hulk Furniture was known to you, the second Formula can be used to get the DSI number.
Consider the Inventory Turnover Ratio for Hulk Furniture Mart was 3 times, and the number of days considered in the reporting period for the computation was 360 days. You will get the Days Sales in Inventory as 120 days. It would then mean that Hulk Furniture takes 4 months on average to convert its inventory to sales.
Now whether this number is high or low totally depends on the industry in which it is operating. In the above example, it is furniture retail. The obtained number can be compared with other peers of similar nature and size in the furniture retail industry to assess the efficiency of inventory management and sales at Hulk Furniture Mart.
How is Days Sales in Inventory (DSI) interpreted?
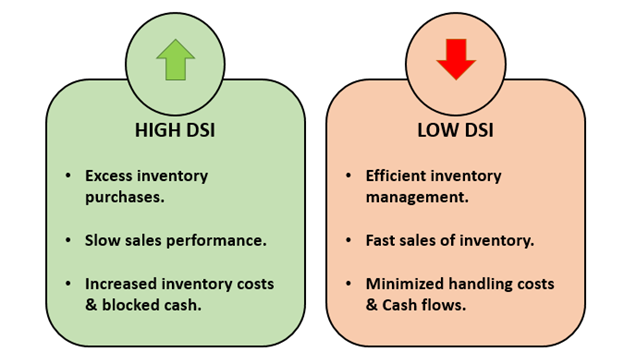
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Lower days of sales in inventory indicate the efficiency of a business in revenue generation and inventory management. It also shows minimization of inventory handling costs and improved operating cash flow.
The exact opposite is reflected by a high DSI number. Higher DSI may sometimes result in inventory becoming obsolete and, in turn, increasing loss. It indicates excess levels of inventory.
How is Days Sales in Inventory (DSI) used?
- DSI is used by analysts and accounting to regulate sales efficiency.
- It shows the time for which cash is tied up in its inventory.
- It is useful in understanding the turnover of goods produced.
- It is useful in deciding optimum inventory levels.
- DSI is a measure of the effectiveness of inventory controls.
- It is useful in gauging the cash efficiency of a business.
- DSI is useful in peer comparison.
- Used by buy and sell-side analysts in computing businesses’ value.
- It is a useful metric for forecasting sales and costs.
- It is an important part of computing the cash conversion cycle.
- Retail firms and companies dealing in perishable commodities assign high value to DSI.
What are the Limitations of DSI?
There are a few issues that may make Days’ Sales in Inventory figure misleading, these are:
- A huge number of adjustments like the write off of inventory affect the DSI.
- The aggregation of all types of inventory that is slow and fast-moving makes it kind of an inaccurate measure.
- If the calculation method is changed significantly, then it becomes incomparable to previous periods, and a retrospective revision may be needed.
- Sometimes firms use an ending balance of inventory which causes the result to differ significantly.
- If the production is outsourced company may report no inventory at all. This will make DSI useless though it may not be in reality.
- If a company tries to reduce priced to increase sale, it may reduce DSI but will definitely adversely affect profitability.
- Sometimes DSI may hide shortages in inventory items because of the presence of other inventory items.
- It is useful for peer comparison but not for cross-industrial comparison of performance.
- DSI measure together with DPO and DSO can be used to gauge the short-term cash flow position of a firm.